Navigating 2025 EPA Regulations: A Business Guide
The 2025 US Environmental Protection Agency Regulations are poised to introduce significant changes in environmental compliance, mandating that businesses across various sectors proactively adapt to new standards, reporting requirements, and sustainability initiatives to ensure operational continuity and avoid penalties.
For businesses operating in the United States, staying ahead of regulatory changes is not just about compliance; it’s about strategic foresight. The forthcoming Understanding the 2025 US Environmental Protection Agency Regulations: A Guide for Businesses introduces a new era of environmental stewardship, demanding a thorough reassessment of current operational practices.
The Evolution of EPA Regulations: A Glimpse into 2025
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) regularly updates its regulations to address evolving environmental challenges, incorporate technological advancements, and align with national and international environmental goals. The 2025 regulations represent a significant step in this continuous evolution, building upon foundational laws like the Clean Air Act, Clean Water Act, and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA). These updates are not merely incremental adjustments; they often reflect a deeper commitment to sustainability, climate change mitigation, and environmental justice. Understanding this historical context provides crucial insight into the philosophy driving the latest changes.
Historically, EPA regulations have moved from a reactive “pollute-and-control” approach to a more proactive “prevent-and-sustain” paradigm. Early regulations primarily focused on setting limits for pollutants and enforcing compliance through penalties. However, as scientific understanding of environmental systems grew, so did the complexity and scope of EPA’s role. We’ve seen shifts towards market-based mechanisms, voluntary programs, and a greater emphasis on source reduction and pollution prevention. The 2025 regulations are expected to further solidify this trajectory, pushing businesses towards more integrated and holistic approaches to environmental management.
One of the key drivers behind the 2025 regulations is the urgent need to address climate change. This manifests in new directives concerning greenhouse gas emissions, energy efficiency, and the promotion of renewable energy sources. Furthermore, the concept of environmental justice, which seeks to ensure that no group of people bears a disproportionate share of negative environmental consequences, is likely to be woven more deeply into regulatory frameworks. This means businesses might face increased scrutiny regarding the siting of facilities, their impact on local communities, and the equitable distribution of environmental benefits and burdens.
Key Regulatory Pillars for 2025 and Their Business Implications
The 2025 EPA regulations are anticipated to be structured around several core pillars, each carrying significant implications for businesses across various sectors. These pillars will likely involve new standards, enhanced reporting requirements, and potentially expanded enforcement measures. Proactive engagement with these areas will be paramount for maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
Air Quality Standards and Emissions Control
The EPA is expected to tighten existing air quality standards, particularly for particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone, and introduce new controls for certain hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). Businesses with industrial facilities that emit air pollutants will need to reassess their emission control technologies and potentially upgrade their systems to meet stricter limits. This could involve investments in new scrubbers, filters, or process modifications to reduce volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful substances.
- Monitoring and reporting: Enhanced requirements for continuous emissions monitoring systems (CEMS) and more frequent, detailed reporting of air pollutant data.
- Permitting adjustments: Review and potential amendment of existing air permits to reflect new abatement technologies and stricter emission limits.
- Compliance costs: Significant upfront capital investments for new equipment and ongoing operational costs for maintenance and monitoring.
Water Quality and Discharge Permitting
Regulations concerning water quality are also slated for updates, focusing on stricter discharge limits for industrial wastewater, stormwater management, and the control of emerging contaminants like PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances). Businesses that discharge water into public waterways or municipal treatment systems will need to review their National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES) permits. This could necessitate new pre-treatment processes or improved stormwater runoff management.
The EPA’s focus on PFAS is particularly noteworthy. These “forever chemicals” have garnered significant attention due to their persistence in the environment and potential health impacts. New regulations might set limits for their presence in industrial discharges, requiring businesses to identify and mitigate PFAS sources within their operations. This could involve supply chain assessments, raw material substitutions, and advanced water treatment technologies.
Waste Management and Circular Economy Initiatives
The 2025 regulations are likely to push businesses further towards circular economy principles, emphasizing waste reduction, reuse, and recycling. This goes beyond traditional waste disposal and management practices, encouraging companies to redesign products and processes to minimize waste generation at the source. New reporting requirements on waste reduction efforts and material flows could become commonplace.
- Hazardous waste updates: Stricter classifications and management requirements for certain hazardous wastes, potentially broadening the scope of what is considered hazardous.
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Potential expansion of EPR schemes, where producers are held responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, including post-consumer collection and recycling.
- Resource efficiency: Incentives and mandates for businesses to improve resource efficiency, reducing raw material consumption and promoting closed-loop systems.
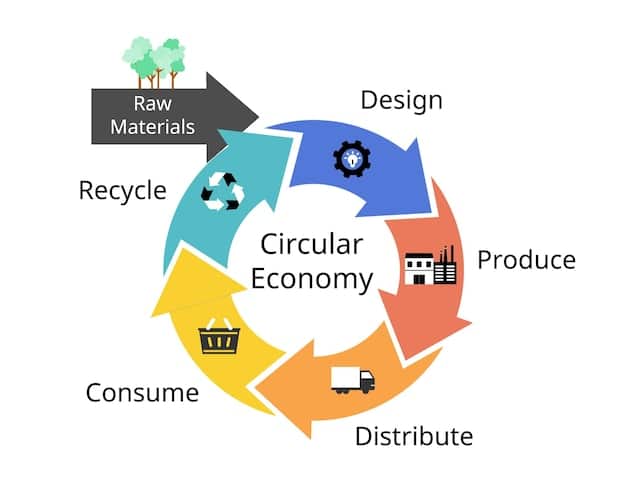
The implications of these changes touch every aspect of a business, from initial product design and procurement to manufacturing processes, waste streams, and end-of-life considerations. Businesses that integrate these principles early will likely gain a competitive advantage.
Understanding Reporting and Compliance Obligations
Beyond the specific environmental standards, the 2025 EPA regulations are expected to introduce more rigorous and technologically advanced reporting and compliance obligations. This shift aims to enhance transparency, improve data quality, and facilitate more efficient regulatory oversight. Businesses should anticipate increased demands on their data collection, management, and submission systems.
The trend towards digital reporting and electronic data submission is likely to accelerate, potentially requiring investment in new software or upgrades to existing environmental management information systems (EMIS). The EPA uses these data streams to monitor compliance, identify trends, and inform future policy decisions. Accurate, timely, and complete reporting is not merely a formality; it is a critical component of demonstrating adherence to the law.
Enhanced Data Collection and Digital Submission
Businesses will likely be required to collect more granular data on their environmental performance, including detailed breakdowns of emissions, discharges, and waste generation. This data will need to be submitted electronically through specific EPA platforms, often accompanied by strict formatting and validation rules. The agency’s push for standardized data ensures it can be readily analyzed and compared across industries.
- Increased frequency of reporting: Some reports traditionally submitted annually might shift to quarterly or even monthly.
- Digital signature and authentication: More stringent requirements for electronic signatures to ensure data integrity and accountability.
- Data quality checks: Automated systems might perform initial data quality checks, flagging inconsistencies or potential errors.
Inspections, Audits, and Enforcement
With expanded regulations often comes a renewed focus on enforcement. Businesses can expect a continued emphasis on routine inspections, unannounced visits, and targeted audits. The EPA utilizes a range of enforcement tools, from administrative orders and civil penalties to, in severe cases, criminal prosecution. Demonstrating a robust compliance program and a culture of environmental responsibility can help mitigate risks.
Furthermore, internal environmental audits will become even more critical for identifying potential non-compliance issues before they are detected by regulatory authorities. These audits should be comprehensive, covering all aspects of a company’s environmental footprint, and should lead to corrective actions where deficiencies are found. A well-documented audit trail can be invaluable in demonstrating due diligence.
Third-Party Verification and Certifications
In some cases, the 2025 regulations might encourage or even mandate third-party verification of environmental data or adherence to certain standards. This could involve independent auditors confirming emission figures, waste diversion rates, or the adoption of specific best management practices. While adding a layer of cost, third-party verification can also enhance credibility and provide an objective assessment of a company’s environmental performance.
Businesses that actively pursue relevant environmental certifications, such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management Systems), might find themselves better prepared for the upcoming regulatory landscape. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to systematic environmental management and can streamline compliance efforts.
Strategic Adaptation: Preparing Your Business for 2025
Proactive strategic adaptation is vital for businesses to navigate the 2025 EPA regulations successfully. Waiting until the last minute can lead to rushed decisions, costly retrofits, and potential penalties. A thoughtful, integrated approach that considers all facets of the business—from operations and supply chain to finance and human resources—will be most effective.
Conducting a Comprehensive Gap Analysis
The first step in preparing for the 2025 regulations is to conduct a thorough gap analysis. This involves comparing your current environmental practices and compliance status against the anticipated new requirements. Identify areas where your operations might fall short, whether in terms of technology, reporting capabilities, or internal processes. This analysis should be granular, looking at specific emission points, waste streams, and operational procedures.
Engage cross-functional teams in this process, including engineering, production, legal, finance, and sustainability departments. Their diverse perspectives will provide a holistic view of your current state and help identify all potential impacts of the new regulations. Use this analysis to prioritize areas for improvement based on risk and potential impact.
Technology Investment and Infrastructure Upgrades
Meeting stricter standards often requires significant investment in new technologies and infrastructure upgrades. This could range from advanced air pollution control equipment and sophisticated wastewater treatment systems to upgraded monitoring devices and IT infrastructure for enhanced reporting. Evaluate the return on investment for these upgrades, considering not only compliance but also potential operational efficiencies and cost savings from reduced resource consumption.
Consider emerging technologies that offer not just compliance but also competitive advantages. For example, process innovations that inherently reduce waste or emissions can avoid end-of-pipe solutions. Investing in renewable energy sources or energy-efficient machinery can help meet climate-related regulations while lowering operational costs in the long run.
Supply Chain and Product Lifecycle Assessment
The scope of environmental responsibility is expanding beyond a company’s direct operations to include its supply chain and the entire product lifecycle. Businesses will need to assess the environmental footprint of their raw materials, components, and finished products. This might involve working closely with suppliers to ensure their practices align with new EPA standards or even seeking out more environmentally sustainable alternatives.
- Supplier audits: Conduct environmental audits of key suppliers to ensure they meet your company’s new standards and regulatory expectations.
- Product redesign: Redesign products to minimize environmental impacts throughout their lifecycle, from material sourcing to disposal.
- Transparency: Be prepared to provide greater transparency about your supply chain’s environmental performance to regulators and consumers.
The Role of Sustainability and Innovation
The 2025 EPA regulations underscore a growing emphasis on sustainability and encourage innovative approaches to environmental management. For businesses, this is not just about meeting minimum compliance; it’s an opportunity to integrate environmental stewardship into core business strategy, fostering innovation, enhancing brand reputation, and potentially unlocking new market opportunities.
Sustainability is no longer a peripheral concern; it is becoming a central driver of business resilience and competitiveness. Companies that proactively embrace sustainable practices often find themselves better positioned to adapt to regulatory changes, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and secure financing from investors with strong Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria. The 2025 regulations will likely reward businesses that can demonstrate a genuine commitment to environmental responsibility beyond mere compliance.
Integrating ESG and Sustainability Frameworks
The 2025 regulations align well with broader Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks that are gaining traction in the investment community. Businesses that integrate ESG principles into their operations and reporting will find it easier to demonstrate compliance and appeal to a wider range of stakeholders. This includes setting ambitious sustainability targets, reporting on progress, and ensuring accountability at all levels of the organization.
Developing a robust sustainability strategy can help businesses identify synergies between regulatory compliance and broader environmental goals. For example, reducing greenhouse gas emissions to meet EPA requirements can also contribute to a company’s net-zero targets and improve its brand image. This integrated approach converts compliance from a burden into an opportunity for value creation.
Fostering Eco-Innovation and Green Technologies
The new regulatory landscape provides a strong impetus for eco-innovation. Businesses that invest in research and development of green technologies, sustainable processes, and environmentally friendly products will not only meet compliance but also gain a significant competitive edge. This could involve developing new materials, optimizing production processes to reduce waste, or pioneering novel pollution control solutions.
- Internal R&D: Allocate resources for in-house research to develop proprietary green technologies and processes.
- Collaborations: Partner with universities, research institutions, and technology startups to accelerate eco-innovation.
- Pilot projects: Implement pilot projects for new sustainable technologies to test their viability and scalability before full deployment.
The regulatory push translates into market demand for solutions that help businesses comply while also being sustainable. Companies that can provide these solutions will find new avenues for growth and expand their market footprint. Innovation can turn regulatory challenges into opportunities for leadership.
Financial Implications and Support Mechanisms
The financial implications of the 2025 EPA regulations can be substantial, encompassing compliance costs, potential penalties for non-compliance, and investments in new technologies. However, businesses should also be aware of various financial support mechanisms and incentives that may be available to help offset these costs and facilitate the transition to more sustainable practices.
Assessing Compliance Costs and Budgeting
Businesses must conduct a detailed assessment of potential compliance costs, including capital expenditures for new equipment, operational costs for increased monitoring and reporting, and expenses related to training and personnel. This requires a robust budgeting process that accounts for both upfront investments and ongoing maintenance and operational outlays. Failure to adequately budget can lead to significant financial strain and potential non-compliance.
Consider the long-term financial benefits of compliance and sustainability as well. Reduced resource consumption, lower waste disposal fees, and avoided penalties can often offset initial investments. Furthermore, a strong environmental performance can enhance access to capital, as banks and investors increasingly consider sustainability metrics. It’s not just about costs; it’s about strategic financial planning.
Grants, Loans, and Tax Incentives
To encourage compliance and environmental improvements, various government agencies at federal, state, and local levels often offer grants, low-interest loans, and tax incentives. These programs can significantly reduce the financial burden of adopting new technologies or implementing sustainable practices. Businesses should actively research and apply for programs relevant to their sector and the scope of their environmental improvements.
- Federal programs: Explore grants and loans from agencies like the EPA, Department of Energy (DOE), and Small Business Administration (SBA) for environmental projects.
- State and local incentives: Many states and municipalities offer their own incentive programs, often tailored to local environmental priorities or specific industries.
- Tax credits: Investigate potential tax credits for investments in renewable energy, energy efficiency, or pollution control equipment.

Navigating the landscape of financial incentives can be complex, often requiring detailed applications and strong project proposals. Consider engaging financial advisors or environmental consultants who specialize in securing such funding to maximize your chances of success.
Legal and Risk Management Considerations
The 2025 EPA regulations will undoubtedly carry significant legal and risk management considerations for businesses. Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, reputational damage, and operational disruptions. A robust legal and risk management strategy is essential to mitigate these potential adverse effects and ensure long-term business viability.
Avoiding Penalties and Litigation
The EPA has broad enforcement powers, including the authority to levy substantial fines, issue cease and desist orders, and even pursue criminal charges for egregious violations. Businesses must prioritize compliance to avoid these penalties. This means not only understanding the regulations but also implementing rigorous internal controls and monitoring systems to ensure continuous adherence.
Beyond direct EPA enforcement, non-compliance can also expose businesses to citizen lawsuits. Environmental groups and affected communities can sue companies for violations of environmental laws, often seeking injunctive relief and compensatory damages. A proactive approach to compliance, coupled with transparent communication, can help reduce the likelihood of such litigation.
Reputational Risk and Brand Image
In today’s interconnected world, a company’s environmental performance can significantly impact its public image and brand reputation. Environmental violations, even minor ones, can quickly become public knowledge through social media and news outlets, leading to negative consumer perception, boycotts, and difficulty attracting and retaining talent. Conversely, a strong record of environmental stewardship can enhance brand value and serve as a differentiator in the marketplace.
Managing reputational risk involves clear and consistent communication about your environmental efforts, transparency in reporting, and prompt, responsible action in response to any incidents. It’s about building trust with your stakeholders by demonstrating a genuine commitment to protecting the environment.
Insurance and Liability Management
Businesses should review their insurance policies to ensure adequate coverage for environmental liabilities. Traditional general liability policies may not cover environmental clean-up costs or third-party damages resulting from pollution incidents. Specialized environmental insurance policies can provide crucial protection against these risks.
Furthermore, conduct regular environmental due diligence, especially during mergers, acquisitions, or property transactions. Unidentified environmental liabilities from past operations can pose significant financial and legal risks. A thorough assessment can help uncover these hidden issues and allow for appropriate risk allocation or mitigation strategies.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 📊 Regulatory Evolution | 2025 EPA rules reflect a shift to proactive sustainability, climate focus, and environmental justice. |
| ⚙️ Business Adaptations | Significant investments in technology, revised operational processes, and supply chain adjustments expected. |
| 📝 Compliance & Reporting | Enhanced data collection, digital submission, and increased enforcement scrutiny are imminent. |
| 💰 Financial & Legal Prep | Budgeting for compliance, seeking available incentives, and managing legal/reputational risks are critical. |
Frequently Asked Questions About 2025 EPA Regulations
The primary goals of the 2025 EPA regulations are to strengthen environmental protection, address climate change, promote sustainability, and ensure environmental justice. These regulations aim to reduce pollution, enhance public health, and encourage more responsible resource management across industries through stricter standards and advanced monitoring.
Small businesses may face particular challenges in adapting to new regulations due to limited resources. The impact could involve increased costs for compliance technologies, new reporting demands, and the need for specialized expertise. However, many EPA programs and state initiatives offer technical assistance and financial incentives specifically for small businesses to aid compliance.
Environmental justice ensures that all people, regardless of race, color, national origin, or income, have equal protection from environmental hazards and equal access to decision-making regarding environmental policy. The 2025 regulations likely integrate environmental justice considerations more deeply, scrutinizing impacts on vulnerable communities and promoting equitable environmental outcomes.
Businesses can find official EPA guidance and resources primarily on the Environmental Protection Agency’s official website (epa.gov). This portal provides access to regulatory documents, compliance assistance tools, technical guidance, and information on grant programs. Subscribing to EPA newsletters and participating in webinars can also keep businesses updated.
The EPA typically provides lead times for new regulations to allow businesses time to adapt. While some regulations may have phased implementation, a formal “grace period” for non-compliance is rare. Businesses should proactively plan and implement changes well in advance of the effective dates to avoid penalties and ensure continuous compliance.
Conclusion
The 2025 EPA regulations represent a critical juncture for businesses in the United States, underscoring a deepening commitment to environmental protection and sustainability. Far from being mere bureaucratic hurdles, these changes offer an opportunity for proactive businesses to enhance their operations, foster innovation, and solidify their standing as responsible corporate citizens. Embracing these regulations as a catalyst for strategic improvement, rather than just a compliance burden, will be key to long-term success.